 |
Angiosperms are classified as either monocots or dicots.
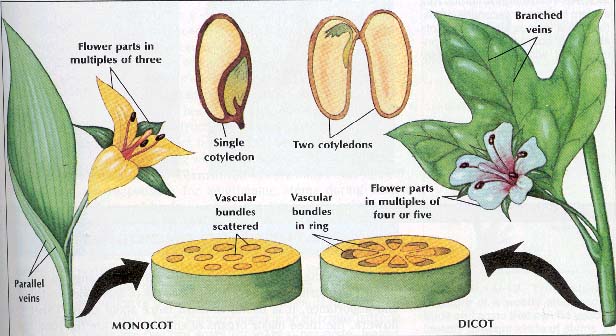
Monocots are plants whose seeds have one cotyledon, a food-storing structure. Seeds of dicots have two cotyledons.
In addition to the number of cotyledons per seed, monocots and dicots differ in other ways. In monocots, vascular bundles, groups of conductive tissue, are scattered throughout the stem, but in dicots, they are arranged in an outer circle. Monocots have long, narrow leaves with parallel veins. Dicot leaves are broad with branched veins. Flower parts of monocots are arranged in threes or multiples of three, but flower parts of dicots are arranged in fours or fives or mulitples of four or five. Common monocots include plants of great value to humans, such as bananas, and cereals such as corn, wheat, rice, and barley. Ornamental flowers that are monocots include tulips, orchids, and lilies. Beans, carrots, peas, and potatoes are dicots. The number of species of dicots is much greater than number of species of monocots.
แหล่งข้อมูล : Biology living system. Page 299.
|
|