 |
Photosynthesis : The Light Reactions and The Dark Reactions
There are two main sets of reactions in photosynthesis. They are known as the light reactions and dark reactions.
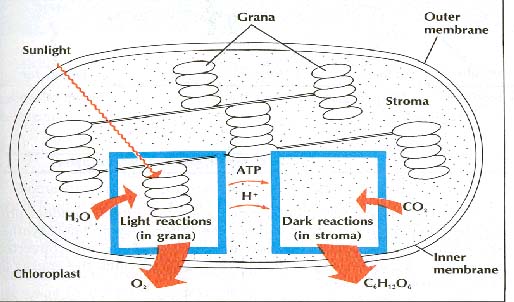
The light reactions involve a series of changes dependent on light. They occur in the grana of chlorophasts of eukaryotes. During these reactions, light is absorbed by chlorophyll and carotene molecules. These molecules trap the energy of light and pass it to a special chlorophyll molecules. Then, by a series of steps, the light energy is converted to the chemical energy of ATP molecules.
Another part of the light reactions involves the water used in photosynthesis. The water molecules are split into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The oxygen is given off as a by-product. The hydrogen ions are used in laser steps of photosynthesis.
Note that the light reactions do not involve carbon dioxide, and no glucose is produced. In summary, the light reaction involves two main events:
1. Light energy is trapped and converted to chemical energy in the bonds of ATP
2. Water is split into hydrogen ions and oxygen.
The events of the light reactions are preparation for the dark reactions. Synthesis of glucose occurs during the dark reactions. The dark reactions do not have to occur in the dark; they simply do not require light.
The dark reactions occur in the stroma of chloroplasts in eukaryotes. During these reaction, carbon dioxide and hydrogen are combined to form glucose. (Glucose is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen-the same elements found in carbon dioxide and water.) This conversion requires energy. The energy comes from ATP. The hydrogen comes from water molecules. Both the ATP and hydrogen used in the dark reactions come from the light reactions.
Although glucose is the main product of the photosynthesis, other important compounds are also made. Some of the glucose can be converted to the fats and amino acids, and some is used directly as an energy source. Glucose transported to other areas of a plant can be stored as starch or converted to cellulose, the substance contained in plant cell walls.
แหล่งข้อมูล : Biology living systems. Page 439.
|
|