 |
Structure of roots
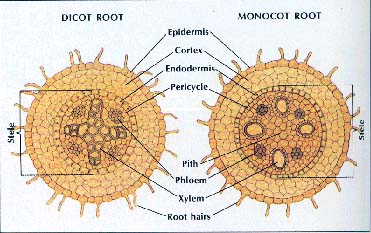
The outer part of an angiosperm root is the epidermis, which protects the root. Root hairs are outgrowths of the epidermis. Much of a root is cortex, which is used for storage. Within the cortex is a central cylinder called the stele. The stele of the root issurrounded by a layer of cells called the endodermis. The outer tissue of the stele is a layer of cells called the pericycle. The pericycle is a kind of meristem . branch roots originate in the pericycle. The inner part of the stele is composed of the vascular tissues-xylem and phloem.
Xylem cells carry water and minerals from the roots to the leaves of the plant. These cell are thick-walled and dead. They are hollow cylinders arranged end to end form a tube. In cross section, they appearas empty circles. Phloem cells carry food made by the leaves to other parts of the plant. These phloem cells are also cylindrical but are not dead. They contain cytoplasm and have thinner walls and a smaller diameter than xylem cells.
In a dicot root, xylem tissue is usually arranged in a star-shaped pattern with phloem vessels between the arms of the star. In a monocot root, the stele is somewhat larger than of the dicot. It contains a great deal of pith tissue in the center. Pith aids in storage of food and water. Large xylem vessels are arranged in a circle around the pith phloem vessels between them.
แหล่งข้อมูล: BIOLOGY living systems. Page 450.
|
|